What Happens in a Male Sports Physical?
Contents
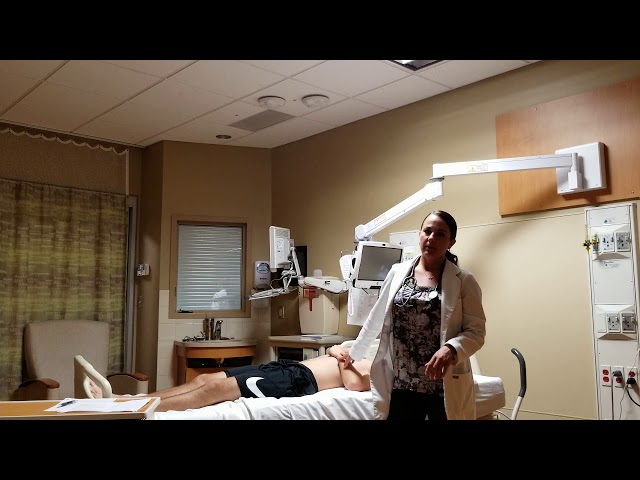
A male sports physical is a thorough exam that looks at a man’s overall health and fitness. The exam includes a review of medical history, a physical exam, and tests to check for any underlying health conditions.
Checkout this video:
The Basics of a Male Sports Physical
Generally, a male sports physical will involve a thorough examination of the applicant’s medical history, a physical examination, and some additional testing if necessary. The physical examination will usually include a vision test, hearing test, heart and lung examination, and a musculoskeletal examination.
Why are they important?
Athletes, both amateur and professional, need to have a sports physical before they start practicing or competing. These physicals help ensure that the athlete is healthy and ready to safely participate in their chosen sport. The physical also gives the doctor a chance to identify any health concerns that could potentially affect the athlete’s performance or put them at risk for injuries.
While most people associate sports physicals with young athletes, they are actually recommended for athletes of all ages. That’s because even if you’ve been playing the same sport for years, your body can go through changes that may impact your safety on the playing field. For example, as you get older, you may be more likely to develop health conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes. If these conditions are not properly managed, they could increase your risk for injuries or other problems during activities.
When should they be done?
Most physicians recommend that young athletes have a sports physical at least annually. For high school athletes, many states actually require a sports physical before they are allowed to participate in sports. Middle school and elementary school athletes may not be required to have a physical, but it is still a good idea. Athletic trainers and coaches should also be aware of the signs and symptoms of common injuries so that they can properly recognize and treat them.
What to Expect
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends that all children have a sports physical before they start playing any type of organized sports. This is to ensure that they are healthy enough to play and that there are no underlying medical conditions that could potentially be exacerbated by playing sports. So, what exactly happens during a sports physical for a male?
Height and weight
Your doctor will take your height and weight to calculate your body mass index (BMI). BMI is a number that shows whether you have the correct weight for your height.
A BMI between 18.5 and 24.9 is considered a healthy weight. If your BMI is below 18.5, you may need to gain weight. If it’s above 24.9, you may need to lose weight.
After your doctor measures your BMI, they will also do a waist circumference test. This measures the amount of fat around your waist. People with more fat around their waist are at higher risk for heart disease and other health problems.
Blood pressure and heart rate
Blood pressure and heart rate will be checked first. You will be asked to remove any clothing that might interfere with the stethoscope or blood pressure cuff. The nurse or doctor will wrap the cuff around your arm and inflate it. This temporarily stops the flow of blood in your arteries so that the heartbeat can be heard more clearly through a stethoscope. The cuff is then released and your blood pressure is recorded.
General appearance and behavior
The health care provider will talk to the teenager about his development, physical activity, diet, and any problems he is having. The health care provider also will ask about family medical history and any medications the teenager is taking.
The health care provider then will do a physical exam. This part of the visit is private, and the teenager will be asked to undress and put on a gown. The physical exam usually includes:
-Height and weight
-Blood pressure
-Vision screening
-Hearing screening
– General inspection of the body, including skin, head, neck, eyes, mouth, nose, ears, chest and abdomen
-Inspection of the genitals (testicles in boys)
-Assessment of behavior and mental development
– Check of joints and muscles for strength and flexibility
Musculoskeletal system
The musculoskeletal system comprises the body’s bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments and joints. The doctor will check for any deformities or injuries and will test your range of motion.
Additional Testing
Sometimes, during a routine physical, the doctor may order additional tests for the patient. This is often the case with men who participate in sports, as there are some tests that are specific to men. This article will cover what happens during a male sports physical and what additional tests may be ordered.
Electrocardiogram (EKG)
An EKG is a test that measures the electrical activity of your heart and can show if you have heart disease. The test is quick, and it usually takes less than 10 minutes. You will need to remove your shirt, and electrodes will be placed on your chest. The electrodes are connected to a machine that records your heart’s electrical activity.
Exercise stress test
An exercise stress test helps doctors see how your heart works during physical activity.
You’ll be asked to walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike. As you exercise, your heart rate and blood pressure will be monitored.
If you have risk factors for heart disease, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease, you may need an exercise stress test to find out if you have coronary artery disease (CAD).
CAD is a condition in which the arteries that supply blood to your heart muscle are narrowed by plaque build-up. This can cause chest pain (angina) or a heart attack.
Blood tests
In addition to the standard urine test, your doctor may also order blood tests. These tests can help to identify any underlying medical conditions that may be causing or contributing to your symptoms.
Some of the most common blood tests used in sports physicals include:
-Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures the number and types of cells in your blood. It can help to identify anemia, infections, and other disorders.
-Lipid panel: This test measures the amount of cholesterol and fats in your blood. High levels of cholesterol can increase your risk for heart disease.
-Kidney function tests: These tests measure how well your kidneys are able to filter waste from your blood. Kidney problems can cause a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, weakness, and dizziness.
-Liver function tests: These tests measure the levels of enzymes and proteins in your blood. Enzymes are produced by the liver and can be elevated when the liver is damaged or inflamed.